The Complete Guide to Industrial Hygiene Assessments

An industrial hygiene assessment is more than just a workplace checkup – it’s an organization’s first line of defense against occupational health risks. Through systematic evaluation of any work environment where there is potential exposure to physical, biological, or chemical agents, these assessments uncover and analyze potential hazards that could impact your employees’ wellbeing. From microscopic air contaminants and toxic substance exposures to noise levels, radiation risks, and poor indoor air quality – a thorough industrial hygiene assessment can be the first step to improving and maintaining workplace safety.
Why Is an Industrial Hygiene Assessment Important?
- Protects workers’ health and safety: Industrial hygiene assessments are fundamental to protecting workers’ health and safety by identifying, evaluating, and controlling workplace hazards before they can cause injury or illness. These assessments help create a comprehensive understanding of potential risks in the work environment.
- Helps avoid costly workplace accidents and health issues: Organizations can significantly reduce financial impact through proper industrial hygiene assessment programs. By preventing workplace accidents and addressing health concerns proactively, companies avoid costly workers’ compensation claims, reduce insurance premiums, and minimize productivity losses due to employee illness or injury.
- Supports compliance with regulatory standards: Regular assessments help organizations maintain compliance with OSHA regulations, industry standards, and other regulatory requirements. This proactive approach helps companies stay ahead of evolving regulations while demonstrating their commitment to maintaining a safe and healthy workplace environment.
Understanding Industrial Hygiene Assessments: Safeguarding Your Workplace
Think of an industrial hygiene assessment as your workplace’s health and safety detective. These crucial evaluations do more than tick compliance boxes—they’re your frontline defense against workplace hazards that could impact your employee’s wellbeing. Drawing from established frameworks developed by OSHA, NIOSH, and AIHA, these assessments transform complex health and safety protocols into actionable insights.
Key Components: The Four Pillars of Workplace Safety
1. Hazard Identification: Uncovering the Hidden Risks
Just as a doctor diagnoses illness, industrial hygienists identify workplace threats before they become problems. Whether it’s chemical exposures that could affect lung function or another occupational hazard, an industrial hygienist’s systematic approach spots potential threats before they impact your workforce.
2. Worker Exposure: Understanding the Human Element
This isn’t just about identifying hazards—it’s about understanding how your team interacts with them daily. Industrial hygienists map out exposure patterns like a detective piecing together a case, identifying high-risk areas and tasks that could compromise worker health and safety. This targeted approach helps prioritize protective measures where they matter most.
3. Occupational Monitoring: Your Workplace’s Vital Signs
Think of occupational monitoring as your facility’s health monitoring system. Using state-of-the-art sampling techniques and instruments, industrial hygienists track everything from air quality to noise levels, creating a comprehensive picture of your workplace’s health. Like a continuous health checkup, this ongoing monitoring catches potential issues before they become problems.
4. Risk Assessment: Strategic Defense Planning
This critical phase transforms raw data into strategic action. Industrial hygienists evaluate each hazard’s potential impact and likelihood, similar to how financial advisors assess investment risks. This clear-eyed analysis helps you allocate resources effectively, ensuring your safety investments target the most significant threats to your workforce’s health and safety.
The Role of Industrial Hygienists: The Guardians of Workplace Health and Safety
Industrial hygienists are the unsung heroes of workplace health and safety, combining scientific expertise with detective work to protect your employee’s. Far from just clipboard-carrying inspectors, these professionals are your frontline defense against workplace hazards, bringing cutting-edge technology and years of expertise to keep your team safe.
1. Hazard Detection: More Than Meets the Eye
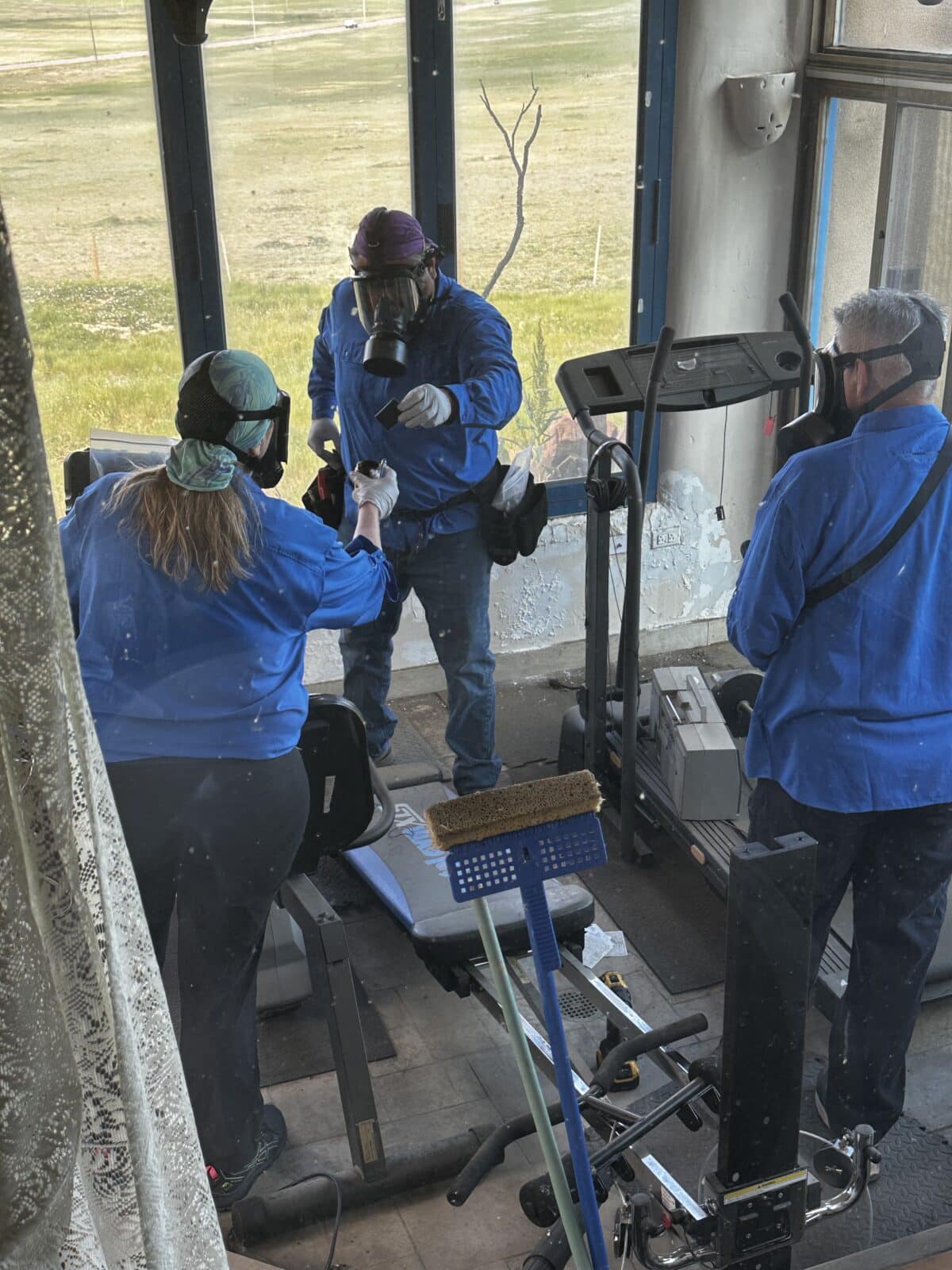
Think of industrial hygienists as workplace detectives with a scientific twist. Armed with advanced monitoring equipment and trained eyes, they uncover hidden threats that could compromise worker health and safety. Whether it’s determining potential exposure issues or identifying subtle ventilation issues, these professionals see what others might miss. They use everything from sophisticated chemical monitoring equipment to air sampling devices, to evaluate worker exposure and developing, actionable data and defensible analytical results.
2. Exposure Monitoring: The Science of Safety
Industrial hygienists don’t just guess at exposure levels—they measure them with precision. Using state-of-the-art monitoring equipment, they track everything from chemical vapors to noise levels, creating a detailed map of workplace exposures. This isn’t just data collection; it’s the foundation for protecting your workforce. They can determine if that new ventilation system is really doing its job or if those hearing protection protocols are truly effective.
3. Control Plan Development: From Insights to Action
Here’s where science meets practical solutions. Industrial hygienists transform their findings into detailed control strategies that work in the real world. They don’t just recommend generic solutions—they craft targeted approaches that consider your workplace’s unique challenges. Whether it’s designing engineering controls that eliminate hazards at their source, implementing administrative controls that change how work gets done, or specifying the exact type of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) needed for specific tasks, their recommendations are both practical and effective.
In the next section, we will dig into the methods and tools used for an effective industrial hygiene assessment, exploring the practical techniques that keep workplaces safe and compliant.
Methods and Tools for Industrial Hygiene Assessments
A professional industrial hygiene assessment relies on proven methodologies and advanced monitoring equipment to protect worker health and safety. Here’s how these essential tools and methods work together to create comprehensive workplace safety evaluations.
Walk-through Surveys: The Foundation of Assessment
Systematic workplace evaluations serve as the cornerstone of effective industrial hygiene programs. These surveys identify potential exposure points, evaluate existing control measures, and document workplace conditions. Industrial hygienists assess ventilation systems, chemical storage protocols, and work processes to build a complete picture of potential workplace hazards.
Sampling Techniques: Quantifying Exposure Risks
Strategic sampling provides concrete data on workplace exposures. Whether through personal monitoring devices worn by workers, handheld monitoring equipment or area sampling stations, these techniques deliver precise measurements of exposure levels. This quantitative approach enables direct comparison with OSHA permissible exposure limits and industry standards, allowing for data-driven decision-making in hazard control.
Direct-Reading Instruments: Real-Time Risk Assessment
Modern direct-reading instruments provide immediate feedback on workplace conditions. These sophisticated tools measure everything from particulate levels to volatile organic compounds, enabling rapid response to changing conditions.
Air Quality Monitoring: Continuous Protection
Fixed monitoring systems provide ongoing surveillance of workplace air quality. These systems track contaminant levels over time, identifying patterns and potential exposure risks before they become significant issues. This data-driven approach enables proactive interventions and helps maintain consistent compliance with safety standards.
Implementing the Hierarchy of Controls in Industrial Hygiene
The hierarchy of controls provides a systematic framework for managing workplace hazards, prioritizing the most effective solutions. Each level represents a different approach to risk management, from complete hazard elimination to personal protection measures.
- Elimination: Completely removing workplace hazards provides the highest level of protection. This approach might involve redesigning processes to remove dangerous chemicals or automating high-risk tasks.
- Substitution: When elimination isn’t feasible, replacing hazardous materials or processes with safer alternatives offers the next best protection level. This could mean switching to water-based solvents instead of organic ones or using mechanical lifting devices instead of manual handling.
- Engineering Controls: These physical changes to the workplace isolate people from hazards. Examples include local exhaust ventilation systems, machine guards, sound enclosures, and radiation shielding.
- Administrative Controls: These procedural changes reduce exposure through modified work practices. Examples include job rotation schedules, timing maintenance during off-hours, and implementing standard operating procedures.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): While PPE is the last line of defense, it plays a crucial role when other controls aren’t sufficient. This includes respiratory protection, chemical-resistant gloves, and hearing protection devices.
Best Practices in Industrial Hygiene Monitoring
Implementing effective monitoring strategies ensures ongoing workplace safety and regulatory compliance:
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular assessment schedules identify exposure changes before they become significant issues. This includes daily checks of critical equipment and quarterly comprehensive evaluations.
- Data Analysis: Systematic review of monitoring data reveals exposure patterns and control effectiveness. This analysis guides decisions about necessary workplace modifications and additional control measures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintaining current knowledge of regulatory requirements ensures monitoring programs meet or exceed standards. This includes staying updated with OSHA regulations and industry-specific guidelines.
- Worker Training: Comprehensive training programs help employees understand workplace hazards and proper control measures. This includes hands-on demonstrations, regular refresher courses, and documentation of training completion.
These integrated approaches create robust safety programs that protect workers while maintaining operational efficiency. The next section will examine industry-specific hazards and targeted control strategies.
Addressing Common Workplace Hazards
Strategies for Specific Industries
In various industries, workplace hazards can differ significantly. Understanding these hazards and implementing customized strategies to manage them is crucial to maintaining a safe environment. Let’s explore common hazards and strategies for specific industries like manufacturing, chemical processing, construction, and agriculture.
Airborne Hazards
Airborne hazards are prevalent across many industries, posing risks through inhalation of dust, fumes, vapors, and gases during routine operations. In manufacturing, processes like grinding or welding can release harmful particles and fumes. Control measures include installing local exhaust ventilation and using respirators and PPE to protect workers.
In the chemical processing industry, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other emissions must be managed. This involves using closed systems for handling chemicals and regular person exposure and air quality monitoring to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Chemical Hazards
Chemical hazards are a major concern in industries that handle toxic substances. In chemical processing, maintaining up-to-date safety data sheets (SDS) for each chemical is essential. Proper labeling and storage practices help prevent accidental exposure.
In construction, workers might encounter hazardous materials like asbestos or lead. Implementing strict protocols for handling and disposing of these materials is crucial.
Biological Hazards
Biological hazards are particularly relevant in industries like agriculture and healthcare. Workers may be exposed to bacteria, viruses, or fungi. For example, in agriculture, handling livestock can pose biological risks. Implementing hygiene practices like regular handwashing and using PPE can reduce these risks.
Healthcare settings require strict infection control measures. This includes using personal protective equipment and proper handling and waste disposal systems to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Ergonomic Hazards
Ergonomic hazards arise from poor workplace design and repetitive tasks. In manufacturing, workers on assembly lines may experience musculoskeletal disorders due to repetitive motions. Adjusting workstation heights and providing ergonomic tools can alleviate these issues.
In construction, tasks like lifting heavy materials can lead to injuries. Training workers on proper lifting techniques and using mechanical aids can help minimize these risks.
Physical Hazards
Physical hazards, such as noise, vibration, and extreme temperatures, are common in industries like construction and manufacturing. Manufacturing environments often have machinery that produces high noise levels. Implementing noise control measures, like sound barriers and providing hearing protection, is essential.
Construction workers might face extreme temperatures or vibrations from heavy equipment. Providing cooling or heating stations and using vibration-damping tools can improve worker safety.
By addressing these common workplace hazards with industry-specific strategies, businesses can create safer environments for their employees. Next, we’ll dig into how enhancing workplace safety and compliance can further protect workers and improve operational efficiency.
Enhancing Workplace Safety and Compliance
Creating a safer workplace involves more than just identifying hazards. It’s about developing robust programs, planning for emergencies, promoting health, and maintaining thorough documentation. Here’s how these elements come together to improve safety and compliance.
Program Development
Program development involves assigning responsibility to a dedicated team or individual who oversees the program. They conduct preliminary exposure assessments and identify areas of concern and potential hazards.
Control measures are then implemented, following the hierarchy of controls: elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment (PPE). By having a structured plan, facilities ensure all potential risks are systematically addressed.
Emergency Response Planning
Having an emergency preparedness and response plan is another foundational piece of every risk control plan. This involves creating detailed procedures for various scenarios, like chemical spills or fires, and communicating with all employees about their roles in an emergency.
Training is key. Regular drills help workers understand the steps they need to take in an emergency. This preparation minimizes panic and facilitates a coordinated response.
Health and Wellness Programming
Promoting health in the workplace goes beyond physical safety. It includes initiatives like wellness programs, vaccination drives, and mental health support. Encouraging a culture of health and wellness helps reduce absenteeism and boosts productivity.
For example, in industries with high physical demands, promoting regular exercise and proper nutrition can improve worker resilience. In office settings, offering ergonomic assessments and stress management workshops can improve overall well-being.
Documentation and Reporting
Keeping detailed records is vital for compliance and continuous improvement. Documentation includes hazard assessments, training sessions, and incident reports. This information helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
Regular reporting ensures transparency and accountability. It also helps in meeting regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines or legal issues. Consistent documentation supports ongoing evaluations and adjustments to safety protocols.
By focusing on these key areas, businesses not only protect their workers but also foster a culture of safety and compliance. This proactive approach leads to a more efficient and harmonious workplace.
Next, we’ll explore the importance of regular assessments and how they contribute to a cycle of continuous improvement.
Find Your Industrial Hygiene Partner Today with Omega
A regular industrial hygiene assessment is crucial for maintaining workplace safety and health. It serves as a proactive measure to identify and mitigate potential hazards before they escalate into serious issues. By routinely evaluating workplace conditions, businesses can ensure a safer environment for their employees and comply with regulatory standards.
Continuous improvement is at the heart of effective industrial hygiene. It’s not just about conducting assessments but also about analyzing the results and making necessary adjustments. This ongoing cycle helps organizations adapt to new challenges and improve their safety protocols over time. Regular assessments provide the data needed to refine control measures, improve worker training, and update emergency response plans.
At Omega Environmental Services, we specialize in providing comprehensive environmental solutions and customized to diverse industries. Our expertise in industrial hygiene assessments helps businesses stay ahead of potential hazards and foster a culture of safety and compliance. With decades of experience, we are committed to supporting our clients in achieving and maintaining high standards of workplace safety.
Get in touch with one of our Industrial Hygienists today for an idea of how we can help you.