Why Is Construction Dust Mitigation Important?
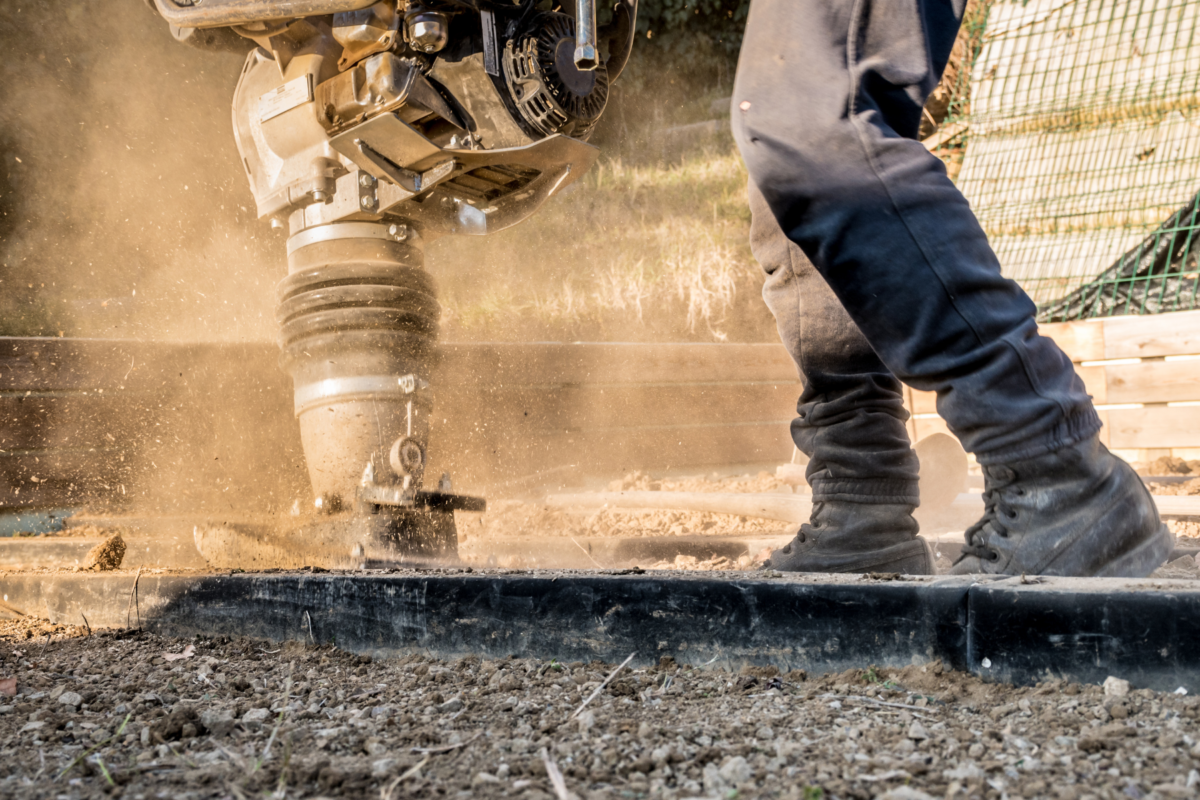

As the secret culprit behind numerous health hazards and environmental concerns, it’s high time we delve into the realm of construction dust mitigation. Every construction project generates dust. Whether it’s the construction of a new large-scale commercial building or the renovation of a historic hotel, construction activity generates fugitive dust, a harmful particulate to human health and property.
The Risks of Fugitive Dust on Construction Sites
Fugitive dust on a construction site can pose several risks, both to the environment and to human health. Here are some of the main risks associated with fugitive dust:
- Air Pollution: Fugitive dust consists of fine particles that can become suspended in the air. These particles, when inhaled, can contribute to air pollution and degrade air quality. Dust particles may contain harmful substances, such as heavy metals, silica, asbestos, or other pollutants, which can have adverse health effects when people breathe them in.
- Respiratory Health Effects: Exposure to fugitive dust can cause various respiratory problems, particularly for construction workers who are directly exposed to the dust. Inhaling fine dust particles can irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and exacerbation of existing respiratory conditions like asthma or chronic bronchitis.
- Allergies and Irritation: Dust particles can act as allergens and irritants, causing allergic reactions, eye irritation, and skin problems. Individuals who are already sensitive or allergic to dust may experience heightened symptoms when exposed to fugitive dust.
- Environmental Impact: Fugitive dust can have negative impacts on the surrounding environment. When dust settles on vegetation, it can hinder plant growth and reduce crop yields. Dust can also accumulate on water bodies, leading to sedimentation, water pollution, and harm to aquatic ecosystems.
- Safety Hazards: Dust accumulation on construction sites can reduce visibility, impairing the vision of workers and equipment operators creating a multitude of environmental and safety hazards. This decreased visibility increases the risk of accidents, such as tripping, collisions, or machinery malfunctions, potentially leading to injuries or fatalities.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Construction sites are often subject to regulations and permits related to air quality and dust control. Failure to adequately manage fugitive dust can result in violations, fines, legal liabilities, and damage to a company’s reputation.
How to Mitigate Dust on Construction Sites
Key techniques for effective construction dust mitigation create cleaner and safer environments on busy construction sites. To mitigate the risks, construction sites should implement effective dust control measures such as using water sprays, dust barriers, windbreaks, and covering materials to minimize dust generation and dispersion. Proper training and personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers are also essential to reduce exposure. Additionally, following relevant regulations and best practices can help ensure the responsible management of fugitive dust on construction sites.
Following the Rules of Dust Control Regulation in California
In California, there are regulations and guidelines in place to address dust control and mitigation on construction sites. The main regulatory agency responsible for enforcing these measures is the California Air Resources Board (CARB), along with local air quality management districts and air pollution control districts. Here are some key regulations and guidelines related to construction dust mitigation and control in California:
- Southern California Air Quality Management District Rule 1466: Rule 1466 aims to reduce the emissions of particulate matter, specifically PM10 (particulate matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or less), from construction and demolition operations in the SCAQMD jurisdiction. PM10 particles can include dust, soot, smoke, and other fine particles that can be harmful when inhaled.
- California Health and Safety Code: The California Health and Safety Code includes provisions related to air pollution control and requires construction sites to take measures to prevent the discharge of dust and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
- California Code of Regulations, Title 17: Title 17 contains specific regulations related to air quality, including requirements for fugitive dust control at construction sites. Section 93105 addresses measures to minimize dust emissions during earthmoving operations, construction activities, and demolition work.
- California Stormwater Quality Association (CASQA) Construction BMP Handbook: This handbook provides Best Management Practices (BMPs) for controlling erosion and sediment runoff from construction sites. It includes guidelines for dust control measures such as erosion control, surface stabilization, and dust suppression techniques.
- Local Air Quality Management District (AQMD) and Air Pollution Control District (APCD) Rules: Each district in California may have its own set of rules and regulations regarding dust control, air quality, and emissions. These rules can vary depending on the specific geographic area and local conditions. Construction sites must comply with the regulations of the respective district where they are located.
- Construction General Permit (CGP): The State Water Resources Control Board (SWRCB) issues a CGP for construction activities that disturb more than one acre of land or are part of a larger common plan of development. The permit includes requirements for erosion and sediment control, which indirectly address dust control by minimizing soil disturbance and runoff.
It’s important for construction site operators to consult with local air quality management districts, as well as the CARB website, and an environmental consultant experienced in construction dust mitigation to understand the specific requirements and guidelines applicable to their project location. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to ensure environmental protection, maintain air quality, and avoid potential penalties or legal liabilities.
South Coast Air Quality Management District Rule 1466
SCAQMD Rule 1466 refers to the South Coast Air Quality Management District (SCAQMD) regulation that addresses the control of particulate emissions from construction and demolition activities. The rule is officially titled “Particulate Matter (PM10) Emissions from Construction and Temporary Portable Equipment.”
Here are some key provisions of SCAQMD Rule 1466:
- Applicability: The rule applies to construction and demolition activities that have the potential to generate PM10 emissions within the SCAQMD’s jurisdiction, which encompasses areas in Southern California, including Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, and San Bernardino counties.
- Dust Control Measures: The rule requires construction and demolition operations to implement dust control measures to minimize PM10 emissions. These measures may include the use of water, chemical dust suppressants, windbreaks, covers, or other effective techniques to prevent or reduce the generation and dispersion of dust.
- Emission Reduction Plans: Construction and demolition projects exceeding certain thresholds must develop and implement an Emission Reduction Plan (ERP). The ERP outlines specific strategies and measures to control PM10 emissions, including dust control practices, equipment requirements, and monitoring procedures.
- Equipment Requirements: Rule 1466 sets emission standards for specific types of equipment used in construction and demolition activities. It includes provisions for controlling emissions from equipment such as bulldozers, backhoes, loaders, concrete pumps, and other portable equipment.
- Recordkeeping and Reporting: The rule requires operators of construction and demolition activities to maintain records of dust control measures implemented, equipment usage, and other relevant information. They may also be required to submit periodic reports to the SCAQMD to demonstrate compliance with the rule.
Construction and demolition contractors in the SCAQMD jurisdiction can familiarize themselves with the specific requirements and provisions outlined in Rule 1466 to ensure compliance and minimize PM10 emissions from their operations.
Call Omega Environmental Today to Stay in Compliance
Navigating California’s dust control regulations can cost a project valuable time. Omega Environmental will provide the necessary assessment and control plan to safely manage fugitive dust on your construction project. Develop a construction dust mitigation plan with Your 24/7 Environmental Partner.
Contact us to learn more about construction dust mitigation!